A watershed is composed of subareas (land areas) and reaches (major flow paths in the watershed). Each subarea has a hydrograph generated from the land area based on the land and climate characteristics provided. Reaches can be designated as either channel reaches where hydrographs are routed based on physical reach characteristics, or as storage reaches where hydrographs are routed through a reservoir based on temporary storage and outlet characteristics. Hydrographs from sub-areas and reaches are combined as needed to accumulate flow as water moves from the upland areas down through the watershed reach network. The accumulation of all runoff from the watershed is represented at the watershed outlet. Up to ten sub-areas and ten reaches may be included in the watershed.
WinTR-55 uses the TR-20 (NRCS 2002b) model for all of the hydrograph procedures: generation, channel routing, storage routing, and hydrograph summation. Figure 10 is a diagram showing the WinTR-55 model, its relationship to TR-20, and the files associated with the model.
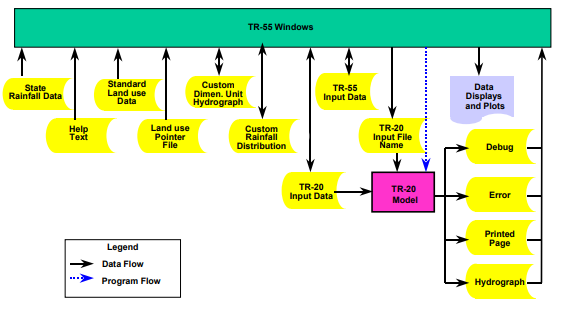
WinTR-55 system schematic (NRCS 2002a)
NRCS. National Engineering Handbook, Part 630 HYDROLOGY, downloaded June 23, 2002